

While descending, it is imperative that divers actively or passively equalize all enclosed air-filled spaces to avoid injury. As the ambient pressure decreases while ascending, the volume of the gas increases proportionately. According to Boyle’s Law, as the ambient pressure increases while descending, the volume of the gas in an enclosed space decreases proportionately. The pressure diminishes by the same amount on ascent. Mechanisms of InjuryĮvery foot of descent in water adds approximately one-half pound of pressure on each square inch of tissue. Ostia blockage can impair drainage and make both descents and ascents troublesome. The ostia can easily be blocked by inflammatory processes, like colds or allergies, and in divers by improper attempts at equalization.

The paranasal sinuses communicate with the nasal cavity via small orifices called ostia (singular: ostium).
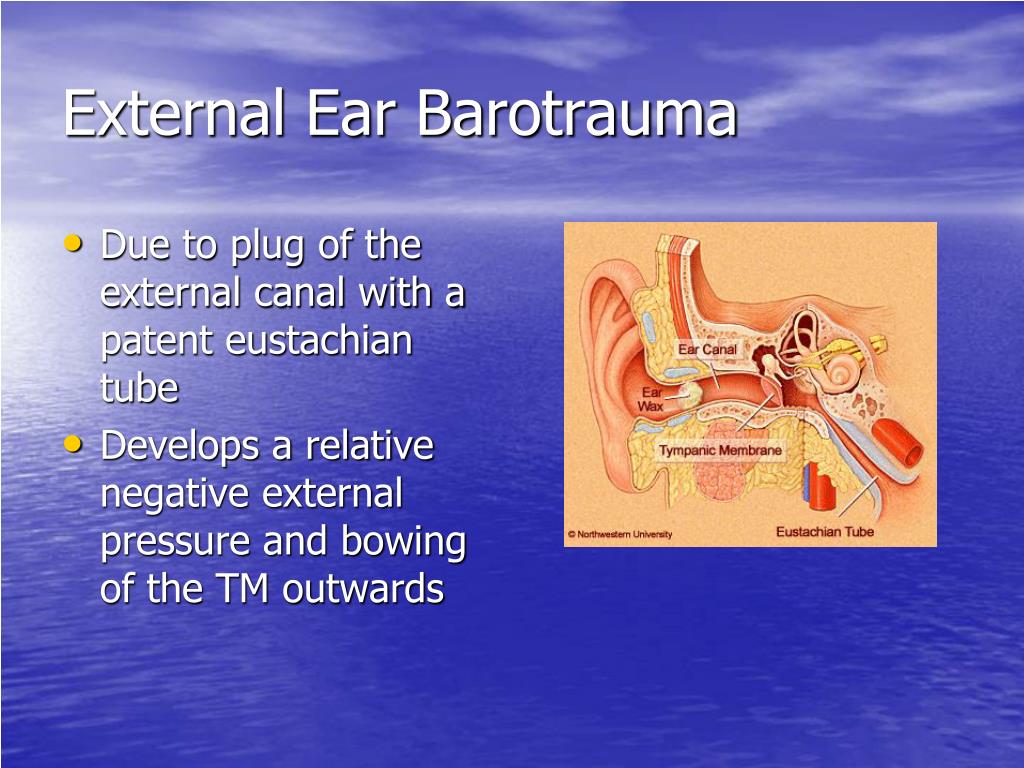
Divers should never underestimate difficulties equalizing sinuses. Although sinus barotrauma is a prevalent and generally benign diving injury, some of its complications could pose a significant risk to the diver’s health. When the paranasal sinuses fail to equalize to barometric changes during vertical travel, damage to the sinus can cause sharp facial pain with postnasal drip or a nosebleed after surfacing. Sinus barotraumas are among the most common diving injuries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
